When working with Git, it is not uncommon to encounter situations where you need to update your local repository with changes from a remote repository. This process is typically achieved using the git pull force command. However, in certain scenarios, you might need to force the overwrite of local files to ensure that your local repository is in sync with the remote repository. This article will guide you through the process of forcing git pull to overwrite local files.
TRENDING
Blisterata: Your Secret Weapon Against Blisters
Understanding the git pull Command
Before diving into the process of forcing git pull to overwrite local files, it is essential to understand how the git pull command works. The git pull command is used to fetch the latest changes from a remote repository and merge them into your local repository. This command is a combination of git fetch and git merge commands.
Fetching Changes from a Remote Repository
The git fetch command is used to retrieve the latest changes from a remote repository. When you run git fetch, Git retrieves the latest commit hashes, branch names, and other metadata from the remote repository. This information is stored in your local repository, allowing you to view the changes made to the remote repository.
Merging Changes into Your Local Repository
After fetching the changes from the remote repository, you need to merge these changes into your local repository. This is where the git merge command comes into play. The git merge command is used to combine the changes from the remote repository with your local changes. If there are any conflicts between the two sets of changes, Git will prompt you to resolve these conflicts manually.
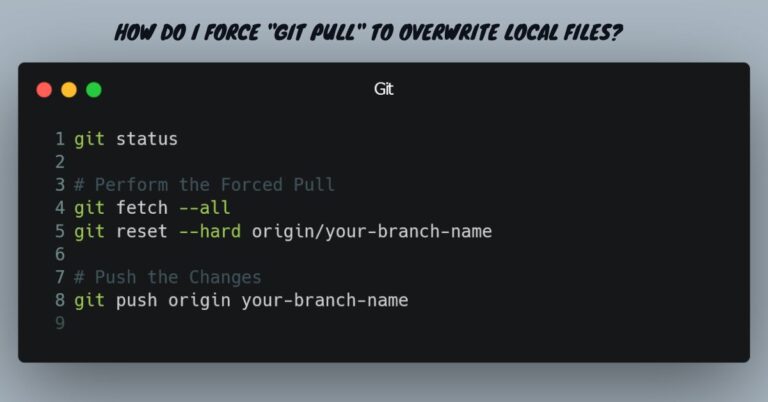
Forcing git pull to Overwrite Local Files
Now that you understand how git pull works, let’s discuss how to force git pull to overwrite local files. There are several ways to achieve this, and the method you choose will depend on your specific use case.
Method 1: Using git pull --force
One way to force git pull to overwrite local files is by using the --force option. This option tells Git to overwrite any local changes that are not committed. Here is an example of how to use this option:
bashgit pull origin master --force
In this example, origin is the name of the remote repository, and master is the name of the branch you want to pull. The --force option ensures that any local changes that are not committed are overwritten.
Method 2: Using git reset --hard
Another way to force git pull to overwrite local files is by using the git reset --hard command. This command resets your local repository to the state of the remote repository, effectively overwriting any local changes. Here is an example of how to use this command:
bashgit reset --hard origin/master
In this example, origin/master refers to the latest commit on the master branch of the remote repository. The --hard option ensures that any local changes are overwritten.
Method 3: Using git clean -df
If you want to remove any untracked files from your local repository before pulling changes from the remote repository, you can use the git clean -df command. This command removes any untracked files and directories from your local repository. Here is an example of how to use this command:
bashgit clean -df
Method 4: Using git stash
If you have local changes that you do not want to lose, you can use the git stash command to temporarily store these changes. This allows you to pull changes from the remote repository without losing your local changes. Here is an example of how to use this command:
bashgit stash
git pull origin master
git stash pop
In this example, git stash temporarily stores your local changes. Then, git pull origin master pulls changes from the remote repository. Finally, git stash pop applies the stashed changes back to your local repository.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how to force git pull to overwrite local files. We have covered several methods for achieving this, including using the --force option, git reset --hard, git clean -df, and git stash. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the method you choose will depend on your specific use case. By understanding how to force git pull to overwrite local files, you can ensure that your local repository is always in sync with the remote repository.
ALSO READ: PS2 Filter AI